Complete guide to energy trading
Energy trading is one of the most popular sectors to trade and invest in, due to the constant supply and demand of energy assets. Crude Oil is perhaps the most traded commodity in the world, and some of the biggest blue-chip companies by market capitalisation are within the energy sector, including PetroChina, ExxonMobil and BP. Learn how to get involved with energy investment.

The energy market: an outline
Energy is an essential service in everyday life. It is needed to heat homes and public places, as well as power mobile phones, computers, cars and public transportation, which society depends on. New technology focuses on producing energy sources that reduce the level of pollution, including renewable energy sources. In fact, it is now reported that this accounts for 25% of total energy generation, in comparison with just 5% in 2006.
Energy trading in the UK comes in various forms. Firstly, you can trade energy stocks within the share market by either buying and selling at spot price or speculating on price action with derivative products such as spread bets or CFDs. Secondly, you can trade a collection of stocks within the same sector through ETF trading, which allows you to diversify your portfolio and spread the risk overall several assets instead of just one share. Thirdly, you can trade physical raw materials, such as crude oil and gasoline, which belong to a highly liquid and volatile commodities market.
The energy market covers a number of products, including oil and gas, renewable energy and electricity. There are also many different stages within the process of trading energy, such as the development, production and shipment of the product. Energy commodities such as crude oil are often sold on wholesale markets, whereas electricity sales usually come from a direct power plant that is owned by a producer. It is common to trade these securities with futures (forward contracts) or options, while energy stocks are exchanged like any other via a stock exchange.
How does energy trading work?
You can invest in the top energy trading companies through shares in the stock market, as well as popular ETFs and energy commodities, such as natural gas, crude oil and heating oil. This can be done through either a spread betting or CFD trading account. Both products are financial derivatives that allow traders to speculate on the price movements of the underlying energy stocks without taking ownership of the asset. You can open a position based on whether you think the price will rise or fall, and depending on which way the markets move, this will result in profit or loss.
Spread betting can be a tax-efficient way to trade in the UK, and this is our most popular method of trading. However, please note that tax treatment depends on individual circumstances and can change or may differ in a jurisdiction other than the UK.
Join a trading community committed to your success
Energy stocks
Traders can buy and sell energy shares in the stock market through share trading, which involves purchasing the stock outright and taking partial ownership of the underlying asset, or they can spread bet and trade CFDs on the price movements of energy share prices. Here are some of the top energy trading companies that investors are watching:
When trading or investing in energy stocks, you should consider all aspects of company fundamentals, including its market capitalisation, share price, P/E ratio and dividend yield. In particular, a high P/E ratio indicates promising results for high-achieving stocks, while a high dividend payout indicates that the company has relatively stable cash flows and balance sheets, which rewards the investor with consistent dividends.
Open an account to start trading on the price movements of energy stocks through spread bets and CFDs.
Renewable energy trading
Particularly in a modern world, there is an increased demand for clean and renewable energy sources that do not harm the planet. These are produced as an alternative to fossil fuels, which has been shown to increase the level of pollution in the atmosphere. Companies such as First Solar and Tesla are focusing on producing more electricity-generated cars, solar power for houses, and clean energy for factories, to name a few. This makes renewable energy trading one of the most popular investments right now, due to the potential of profitable returns. Learn more about trading renewable energy stocks here.
Energy ETFs
Exchange traded funds (ETFs) are investment funds that grant a trader better access to underlying assets, including shares within a particular market. ETFs aim to track an index of global stocks that belong to the energy sector. Here are some ETFs that track top performing blue-chip and large-cap stocks in the global energy market:
An advantage of energy ETFs is that they help to spread the risk of trading energy stocks across several assets, depending on the index size. This means that if the performance of one stock declines, the others will help to offset damage to the overall performance of the fund. This can also help to diversify your overall portfolio, as you will be trading multiple assets at once. However, trading on energy ETFs still brings the common risks of market volatility, as well as slippage and gapping that often occurs within the stock market. Traders should stay vigilant when analysing price charts for this reason, as exchange-traded funds can become just as volatile as regular indices.
Open an account to start spread betting or trading CFDs on energy ETFs.

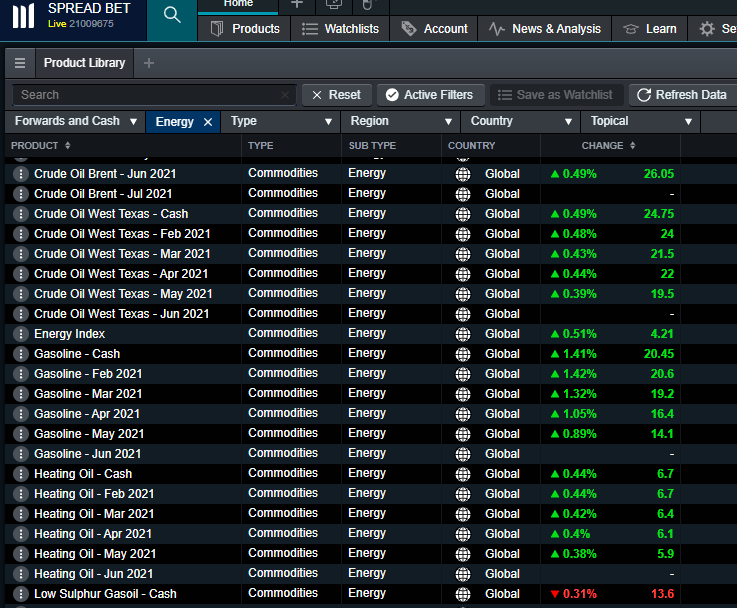
How to trade energy commodities
Our commodities market has some of the most popular and profitable instruments on our platform, due to market volatility and investors treating various commodities as a safe haven. Energy commodities that are available to trade include:
When trading two similar assets such as crude oil Brent vs WTI, many traders choose to adopt a pairs trading strategy. This involves opening a long positon at the same time as shorting another, in order to offset risk caused by one of the assets. This is particularly effective within the energy commodities market, as crude oil prices can be volatile and supply and demand can drop rapidly, due to many external factors.
Open an account to start trading on energy commodities. You can also trade on our Energy Index, which is a product exclusive to CMC Markets. This commodity index is made up of 6 types of energy, including both Crude Oil Brent and WTI, Low Sulphur Gasoil, Natural Gas, Gasoline and Heating Oil. Spread betting or trading CFDs on a commodity basket can help to diversify your portfolio.
Increase your exposure to the commodity market
EXCLUSIVE TO CMC
Expecting big things in energy? Diversify your portfolio and spread risk with our unique commodity indices, which allow you to take a view on a commodity sector as a whole with a single position.

How to become an energy trader with CMC Markets
Trading on the price movements of energy stocks and ETFs starts by registering for a live account. Energy commodities are available to trade on a live account, but you can also practise with virtual funds beforehand on our trading demo account. This will ensure that you are familiar with our platform, along with risk management tools such as setting stop losses and take profit orders, before placing trades in a risky market.
Energy trading platform
Our clients can trade on the price movements of more than 7750 shares and ETFs on our award-winning online trading platform, Next Generation, as well as over 90 sought-after commodities. You can study the price action of your positions using our customisable charts, and make the most of our drawing tools, technical indicators and price projection tools. We also have various sections that are dedicated to news reports for the energy market, as well as a dedicated chart forum, where traders can share ideas and strategies for trading within this sector. Learn more about our charting features.
Energy market news
It is important to keep up to date with the latest news releases and changes within the financial markets. Our news and analysis section of the platform is dedicated daily updates from experienced market analysts, and our news and insights section provides external information. This includes economic announcements from Reuters and fundamental analysis reports on company shares from Morningstar.